Rising electricity costs have made energy efficiency a top priority for households and businesses alike. Cooling systems, once considered unavoidable power guzzlers, have undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years. Thanks to technological advancements, modern cooling solutions are now smarter, more efficient, and significantly less expensive to operate than their older counterparts. Understanding how these systems work can help consumers make informed decisions and reduce their monthly electricity bills without sacrificing comfort.
This article explores the technologies, design improvements, and usage strategies that enable modern Air Conditioner to deliver powerful cooling while consuming less energy.
The Evolution of Cooling Technology
In the past, cooling units relied on simple on-off mechanisms. When the temperature rose above a set point, the system would turn on at full power, and once the target temperature was reached, it would shut off completely. This cycle repeated frequently, leading to high energy consumption, temperature fluctuations, and excessive wear on components.
Modern systems, by contrast, are designed with energy efficiency at their core. Innovations in compressors, electronics, sensors, and materials have reshaped how cooling is delivered. Instead of brute-force cooling, today’s systems focus on precision, adaptability, and optimization.
Inverter Technology: A Game Changer
One of the most significant breakthroughs in cooling efficiency is inverter technology. Traditional units operate at a fixed speed, while inverter-based systems adjust their compressor speed based on real-time cooling demand.
When a room approaches the desired temperature, the compressor slows down rather than turning off. This steady operation reduces power spikes, maintains consistent temperatures, and dramatically lowers electricity usage.
Benefits of Inverter Technology
-
Reduced energy consumption
-
Stable indoor temperature
-
Lower noise levels
-
Longer system lifespan
Energy Consumption Comparison

This graph visually demonstrates how inverter systems consume less power over time by avoiding frequent starts and stops.
Higher Energy Efficiency Ratings
Energy efficiency ratings play a crucial role in determining how much electricity a cooling system uses. Modern units are designed to meet or exceed stringent efficiency standards, often labeled with star ratings or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios (SEER).
Higher-rated systems may cost more upfront, but they repay that investment through lower monthly bills. A high-efficiency unit can consume 30–50% less electricity than an older, lower-rated model.
Consumers who replace outdated systems with high-efficiency models often notice immediate reductions in energy costs, especially during peak summer months.
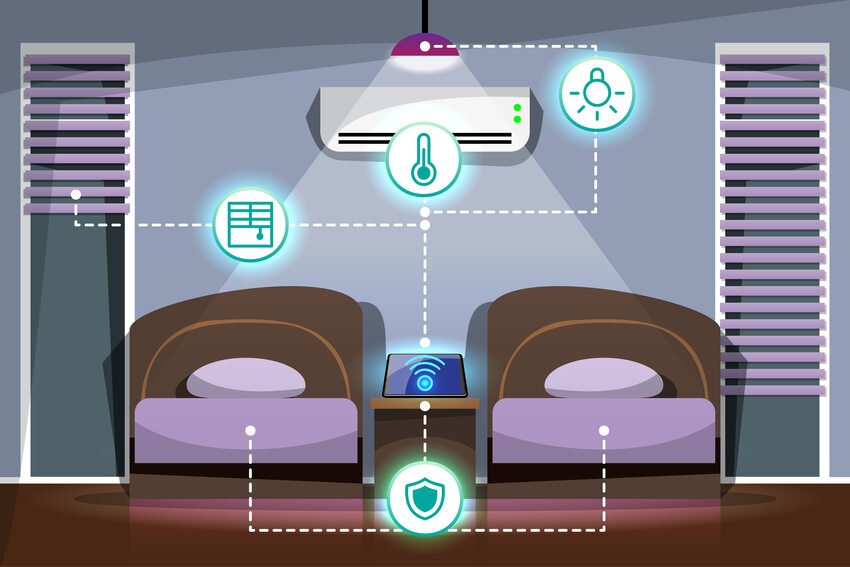
Smart Sensors and Adaptive Cooling
Modern cooling systems use advanced sensors to monitor room temperature, humidity, occupancy, and even sunlight exposure. These sensors allow the system to adjust cooling output dynamically, ensuring energy is used only when necessary.
For example:
-
If a room is unoccupied, cooling output can be reduced automatically.
-
At night, systems can shift to energy-saving modes.
-
During mild weather, minimal cooling is applied instead of full-capacity operation.
This intelligent behavior ensures that energy is not wasted on unnecessary cooling.
Improved Compressor and Motor Design
Compressors and motors are the heart of any cooling system. Modern designs focus on efficiency, precision engineering, and reduced friction. Variable-speed compressors, brushless motors, and improved lubrication techniques all contribute to lower energy consumption.
These components not only draw less power but also generate less heat during operation, further improving overall efficiency. Reduced mechanical strain also means fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs over time.
Better Insulation and Heat Exchange
Heat exchange efficiency plays a vital role in how much energy a system consumes. Modern units use advanced materials and optimized coil designs to improve heat transfer between indoor and outdoor environments.
Enhanced insulation minimizes energy loss, while larger and more efficient heat exchangers allow faster cooling with less power. As a result, systems achieve desired temperatures quicker and maintain them with minimal energy input.
Smart Controls and Connectivity
The integration of smart technology has revolutionized how users interact with cooling systems. Mobile apps, Wi-Fi connectivity, and programmable thermostats give users precise control over their energy usage.
Key advantages include:
-
Scheduling cooling based on daily routines
-
Remote control to avoid unnecessary operation
-
Energy usage monitoring and optimization suggestions
By aligning cooling schedules with actual usage patterns, users can prevent energy waste and significantly lower electricity bills.
Energy Savings with Smart Scheduling
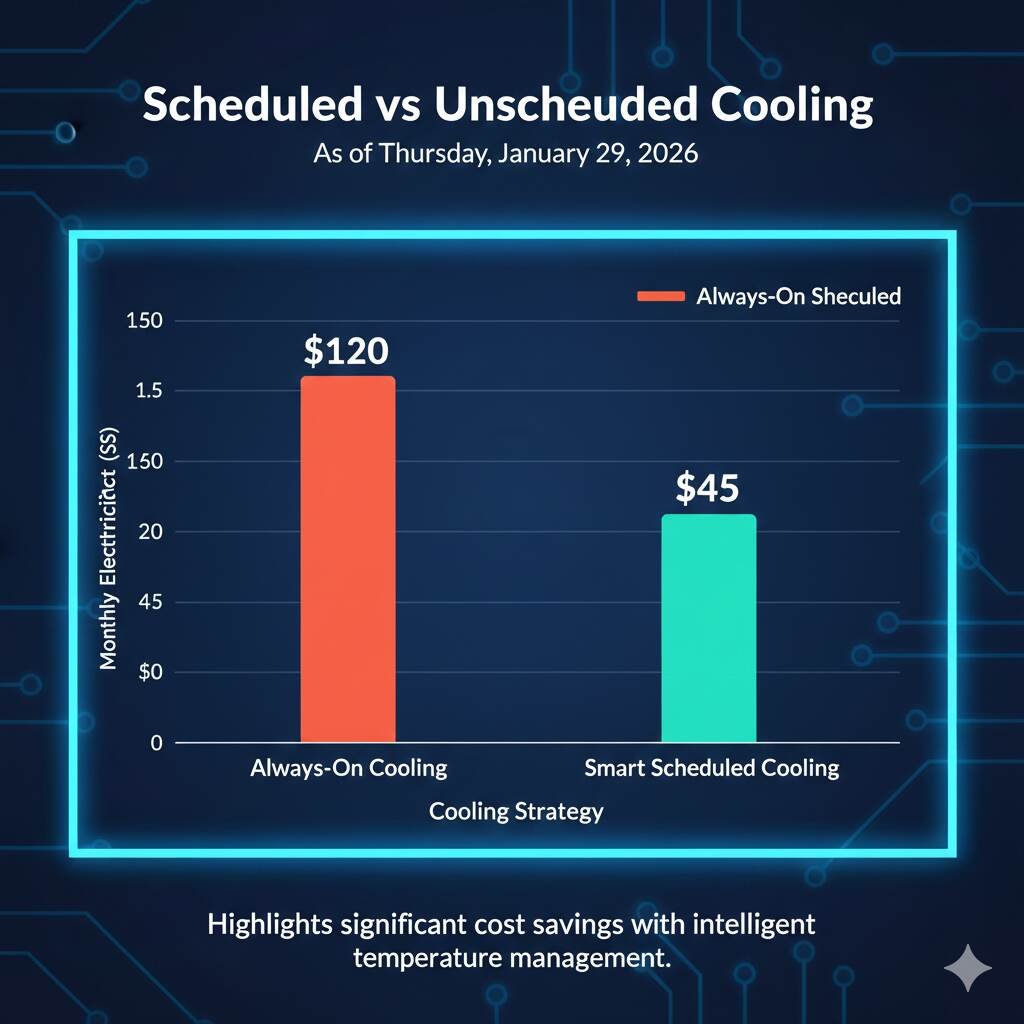
This graph highlights how intelligent scheduling leads to measurable cost savings.
Eco-Friendly Refrigerants
Modern cooling systems use environmentally friendly refrigerants that are more efficient at heat absorption and release. These refrigerants require less energy to achieve the same cooling effect compared to older chemical alternatives.
Improved refrigerants not only reduce electricity usage but also have a lower environmental impact, aligning energy savings with sustainability goals.
Zoning and Customized Cooling
Zoning systems allow different areas of a home or building to be cooled independently. Instead of cooling the entire space uniformly, users can focus cooling only where it’s needed.
For example:
-
Bedrooms can be cooled at night while living areas remain inactive.
-
Office spaces can be cooled during work hours only.
This targeted approach minimizes unnecessary energy use and enhances comfort.
Reduced Maintenance-Related Energy Loss
Poorly maintained systems consume more electricity due to clogged filters, dirty coils, and inefficient airflow. Modern designs simplify maintenance and often include self-diagnostic features that alert users when service is needed.
Clean filters, efficient airflow, and optimized performance ensure that the system operates at peak efficiency, preventing gradual increases in power consumption.
Long-Term Cost Savings
While modern cooling systems may require a higher initial investment, their long-term financial benefits are substantial. Lower electricity bills, reduced maintenance costs, and longer lifespans combine to deliver significant savings over time.
Homeowners who upgrade to modern solutions often recover their investment within a few years through reduced energy expenses alone.
Conclusion
Modern cooling technology has transformed the way we manage indoor comfort. Through inverter technology, smart sensors, high-efficiency components, and intelligent controls, today’s systems deliver powerful cooling while consuming far less energy than older models. By understanding these advancements, consumers can make informed choices that reduce electricity bills without compromising comfort.
As energy costs continue to rise, investing in efficient solutions is no longer optional—it’s a smart financial and environmental decision. Modern Air Conditioners prove that comfort and cost savings can go hand in hand when technology is used wisely.
FAQs
Q1: Do modern air conditioning systems really save electricity?
Yes. Advanced technologies like inverter compressors, smart sensors, and efficient motors significantly reduce energy consumption compared to older models.
Q2: Are inverter systems worth the higher upfront cost?
In most cases, yes. The electricity savings over time often outweigh the initial price difference.
Q3: How much can I save by upgrading to a modern system?
Savings vary, but many users report 30–50% reductions in cooling-related electricity bills.
Q4: Do smart features really help lower energy usage?
Absolutely. Scheduling, remote control, and usage monitoring help prevent unnecessary operation and reduce waste.
Read Dive is a leading technology blog focusing on different domains like Blockchain, AI, Chatbot, Fintech, Health Tech, Software Development and Testing. For guest blogging, please feel free to contact at readdive@gmail.com.